The Ultimate Guide to Improving Operational Efficiency

Economic unpredictability and volatility have forced organizations across the globe to evaluate how they can become more efficient and productive while spending less and using resources more wisely. Widespread uncertainty has also led many companies and firms to cut spending — whether that means implementing hiring freezes or layoffs or engaging freelancers and independent consultants.
Continuous change doesn’t always have to be viewed negatively, though. Rather, you can use uncertainty to your advantage. By optimizing for productivity and efficiency, your organization will benefit from the effective use of resources, less waste, more time to spend on high-value strategic work, and most importantly, improved ROI. The way to achieve this is through operational efficiency.
Table of Contents:
- What is operational efficiency?
- How to Increase Operational Efficiency
- Operational Efficiency Strategies
What is operational efficiency?
Operational efficiency is the process of improving productivity and streamlining operations across an organization to reduce friction, redundancy, and/or waste all while offering the best possible products/services and customer experiences.
It allows your business to trim or cut unnecessary costs and use only the necessary resources to successfully create a product/service of the highest quality that improves ROI.
Understanding Operational Efficiency
Operational efficiency is often referred to as a metric that you track to determine your efficiency of profit earned as part of operating costs. Although this is accurate, operational efficiency shouldn’t just be a metric — it should be thought of as an operating model which sits among people, process, and technology and is rolled out across your organization. It can serve as a guiding light throughout strategic planning processes, transformations and operations management, and strategy execution.
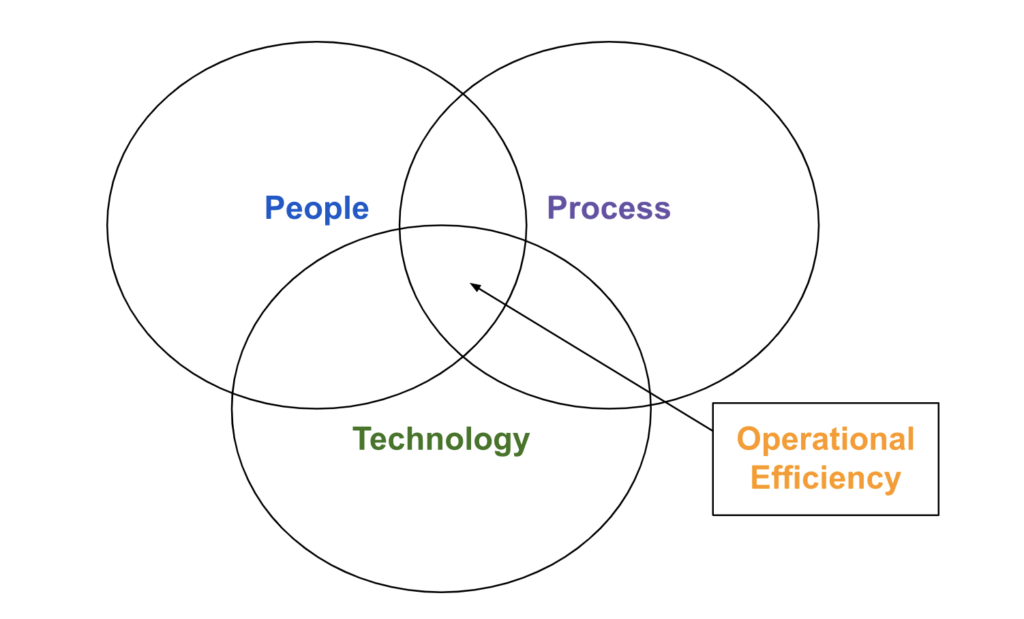
How to Increase Operational Efficiency
To improve operational efficiency, you’ll first need to understand its components and how to measure them. Then you can invest in change management and begin implementing operational efficiency strategies across your organization.
1. Measure operational efficiency.
There isn’t one specific way to measure operational efficiency. However, there’s a commonly-used formula that is also referred to as the operational efficiency ratio. This formula provides insight into how operationally efficient your company is. The purpose of the formula is to surface trends in your efficiencies and inefficiencies over time and ultimately identify the areas in which resources can be reallocated and waste can be reduced.
The formula requires you to add your operating expenses and divide the sum by your total revenue. If you then multiply by 100, you’ll have your operational efficiency rate.

Operational Efficiency Metrics
Operational efficiency metrics and KPIs are how companies can measure productivity as well as ensure resources are not being wasted. In addition to measuring your operational efficiency rate, there are other metrics you may choose to track to get a better understanding of your success and areas for improvement.
For example, Dan Dodd, an Expert on Catalant’s Expert Marketplace, recommends looking at your inventory turns. “Inventory is waste that is readily visible, and on every balance sheet. Inventory readily relates mathematically to return on equity and stock price, but the impact on quality is even more significant.”
Here are some additional operational efficiency KPIs to consider tracking:
- Operating expenses
- Capital expenditures
- Human capital expenses
- Revenue
- Customer satisfaction score
We’ll also discuss some strategies that include some of these KPIs that you can deploy later in the post to maintain operational efficiency.
2. Invest in change management.
“The biggest obstacle when incorporating operational efficiency across the business is change management,” says Melanie Espeland, a consultant on Catalant’s Expert Marketplace. “Transparent communication including your leadership’s ‘why’ for change is critical to bringing along your employees. If you do this, you can not only succeed but create intrapreneurs who become champions of operational efficiency and the required changes for success.”
To drive this point home, leaders from Highmark Health shared in a webinar that in order to successfully drive change at scale, you must first look at your culture and then tailor your new program accordingly. For example, an analysis of Highmark’s culture gave leaders the insight to use a bottom-up approach beginning at the business unit level when deploying their new program rather than a top-down approach.
3. Prioritize strong communication.
To achieve operational efficiency, maintaining strong lines of communication across the business from the top down and vice versa as well as cross-department is key. You can use technology and tools to automate data entry and streamline daily communications to help employees stay efficient.
Strong communication makes the process of change management, discussed above, and gaining employee buy-in, easier to achieve. It also allows your team to standardize the process of training current and new employees and make for more effective and enjoyable conversations with and for your clients.
4. Use operational efficiency strategies and evaluate and iterate on them.
Finally, use operational efficiency strategies. In the next section, we’ll review some commonly-used strategies. These are crucial to your ability to improve operational efficiency and roll the process out across your organization. Don’t be afraid to test different strategies to identify the one(s) that works best for your organization and its people.
Operational Efficiency Strategies
When determining which operational efficiency strategy (or strategies) you might deploy, think about what your organization’s efficiency goals are and determine which strategy is most likely to help you successfully and quickly achieve those targets.
1. Strategic Flexibility
In a new world where changes outpace regular planning and execution styles, new agile capabilities for strategic operational management must be established to enable executives to identify, assess, and concretely respond.
Andrew Karpie
That’s why operationally efficient organizations leverage strategic flexibility as a core capability.
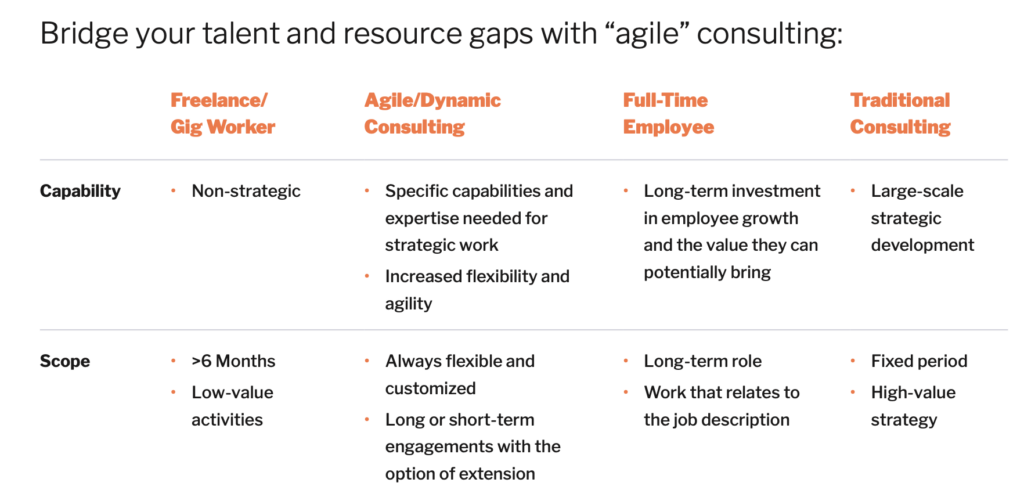
Strategic flexibility, also referred to as agile consulting, helps you navigate today’s quick market shifts by planning for shorter time horizons, adopting agile ways of working, and bringing alternatives to the table such as the use of independent talent. Strategic flexibility enables resiliency against today’s volatile dynamics by giving leadership access to a strategic marketplace platform, like Catalant’s Expert Marketplace, to find experienced independent talent who can solve discrete business problems despite today’s broadly felt and time-sensitive human capital or capacity challenges.
According to Joe Fuller, Professor of Management Practice and Co-head of the Managing the Future of Work Project at Harvard Business School, the key to success when implementing strategic flexibility at any organization is focusing on training among managers and directors. In doing so, you’ll teach those leaders how to master the skill of accommodating outside talent and plugging in the capability of strategic flexibility alongside your other talent operating models such as full-time hires and traditional consultants).
2. Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma is an operational and managerial approach that’s meant to eliminate any types of resource waste and errors to improve overall performance. It brings together Six Sigma (which entails making statistical improvements to a business process and the use of qualitative measurements) and lean philosophy (which entails focusing on value creation and eliminating processes that don’t directly impact the final product).
By implementing Lean Six Sigma at your organization, you’ll get rid of the resources that don’t create value for your customers — this includes both tangible and intangible resources such as talent, a high-quality product, time, and effort.
3. Zero-based Budgeting
Zero-based budgeting has recently become increasingly popular. For businesses, specifically, it means your budget starts from scratch, or a “zero base,” each year. Then, every aspect of the business is analyzed, line by line, for its needs and costs. Using this approach, every line of business within an organization is analyzed for its needs and costs while ignoring historic spending. Then each line and its impact must be justified in order to have funding approved.
Since each line of the budget is analyzed, zero-based budgeting creates greater budget efficiency and flexibility. It also makes it clear which activities generate the most revenue so those can be prioritized.
4. Enterprise Resource Planning and Supply Chain
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) refers to how all aspects of a company interact with each other when “managing efficient resource use.” When an ERP system comes together with supply chain processes, suppliers understand your goals and systems. As a result, ERP will streamline supply chain management and allow your organization and suppliers to work closely together to ensure resources are available at a low cost when you need them. Your team may also leverage data integration to inform your suppliers of when you may be in need of resource inventory so they can proactively manage your supply.
5. Process Improvement
To achieve operational efficiency, your organization must consistently look for ways to streamline and refine day-to-day processes. Ask the leaders of different departments how their team members spend their time — are there any processes that are critical to their roles that require more resources and time than preferred? Determine whether any of those tasks could potentially be taken off their plate through workflow and process automation.
If not, work with department heads to identify solutions that could make those tasks more efficient — do employees have the right technology to enable the completion of those tasks? Does communication need to be improved? Can a new strategic approach to those responsibilities be tested? Can talent across those tasks and responsibilities be used differently?
6. Technology
There are many tools that support automation for process improvement and help increase operational efficiency in other ways. For example, project management tools automate workflows to give help team members stay productive and manage time wisely. A service management system (SMS) integrates organizational and operational management data and information.
An SMS makes for a single source of truth when it comes to details about processes and planning. This is also important to ensure your team is able to accurately report on and analyze data about all aspects that relate to the organization’s operations, finances, and project management.
Ready to implement best practices for operational efficiency at your organization?
Let’s TalkRelated Articles
Share Article